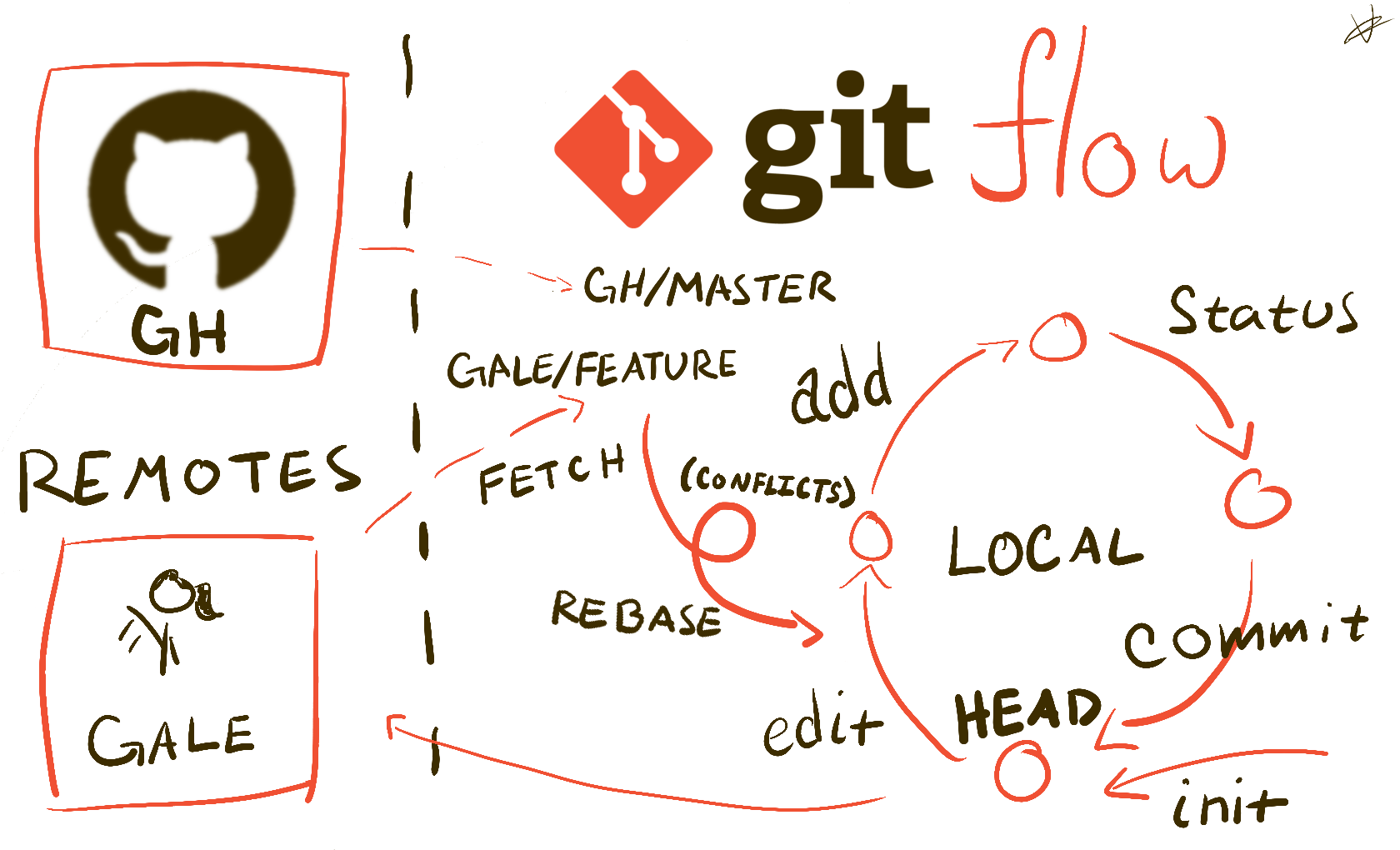
How To Git
Elijah C. Voigt
NAME
git - the stupid content tracker
SYNOPSIS
git <command> [<args>]
DESCRIPTION
Git is a fast, scalable, distributed revision control system
with an unusually rich command set that provides both
high-level operations and full access to internals.